This response was written by John Lott and webbed by David Friedman. Lott is responsible for contents; Friedman for formatting.
Claim #1: "The Study uses
incorrect and discredited methology"
a) The use of the
arrest rates in explaining crime rates
Teret provides a very biased reading of the
National Academy of Sciences report. For example, Vanaele (p. 281)
concluded that: "the negative relationship between the crime rate and
the probability of imprisonment and between the crime rate and the
time served is not spurious." The sociologists on the panel were more
cautious but still concluded (pp. 4 and 7) that, "Taken as a whole,
the evidence consistently finds a negative association between crime
rates and the risks of apprehension, conviction or imprisonment. . .
. the evidence certainly favors a proposition supporting deterrence
more than it favors one asserting that deterrence is absent."
I think that there are also important theoretical reasons for
including variables like the arrest and conviction rates as well as
prison sentence lengths. Prior to my work none of the papers on gun
control had attempted to account for the impact of these factors on
the crime rate. In any case, the original paper and my book also
reported the results with the arrest rates excluded. Even other
critics such as Black and Nagin have claimed (December 6, 1996, p. 5)
that: "The absence or presence of the arrest ratio has little impact
on the coefficient estimates in the model."
b) "The reductions
in violent crime that the authors attribute to the laws may simply be
a commonly-observed downward drift in crime rates toward some
long-term average level."
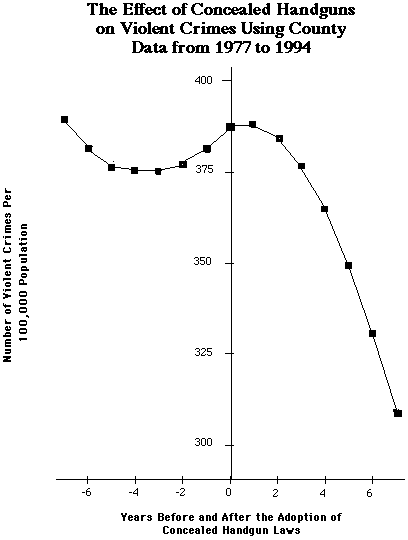
To illustrate that the results are not merely
due to the "normal" ups and downs for crime, the accompanying figure
shows the pattern of violent crime before and after the adoption of
the shall-issue laws.1 The declines not only begin right
when the concealed-handgun laws pass, but the crime rates end up well
below what they were prior to the law.

The original study as well as the book also included not only individual state and county time trends (p. 25, fn. 53 and pp. 34-37), but also a separate variable for each individual year to allow for any possible pattern in national crime rate trends over the 16 years studied in the original paper and 18 years studied in the book. In addition, different crime rates to explain the changes over time in the crime rates studied (pp. 31-34). Given the high correlation over time between different violent crime rates or between different property crime rates, this picks up most crime cycles.
Claim #2: "The Study's
results depart from well-established criminologic theory and facts
about crime."
a) The strongest effects should be
for robbery
I have two responses. First, as anyone who has carefully reads my
work will know, it is simply not true that the results show "little
or no effect on robbery rates." Whether the effect was greater for
robbery or other violent crimes depends on whether one simply
compares the mean crime rates before and after the laws (in which
case the effect is relatively small for robbery) or compares the
slopes before and after the law (in which case the effect for robbery
is the largest).
Second, it is not clear that robbery should exhibit the largest
impacts primarily because "robbery" encompasses many crimes that are
not street robberies. For instance, we do not expect bank or
residential robberies to decrease, and, in fact, they could even
rise. Allowing law-abiding citizens to carry concealed handguns makes
street robberies more difficult, and thus may make other crimes like
residential robbery relatively more attractive. Yet, not only
is it possible that these two different components of robbery move in
opposite directions, but to rank some of these different crimes one
requires information on how sensitive different types of criminals
are to the increased threat.
Making claims about what will happen to different types of violent
crimes is much more difficult than predicting the relative
differences between, say, crimes where criminals have no contact with
victims and those crimes where they do. Though even here some of
these questions cannot be settled a priori. For example, it is
possible that when violent crimes decline more people feel free to
walk around in neighborhoods, which implies that they are more likely
to observe the illegal actions of strangers. Criminals who commit
violent crimes are also likely to commit some property crimes, and
anything that can make an area unattractive to them will reduce both
types of crime.
Claim #3: "The Study does not
account for the effects of other important gun laws."
This is simply wrong. Both the original paper and
the book account for a wide array of different gun laws: state
waiting periods, the length of state waiting periods, state
background checks, the Brady Law, and penalties for using guns in the
commission of crime. Indeed, my work is the first attempt to provide
systematic national data on these questions. When one looks at these
other gun laws there is no evidence that they reduce violent crime
rates. If anything, there is some evidence that the Brady Law
slightly increased rape and aggravated assault rates because the
waiting period makes it difficult for a few people to quickly obtain
a gun for self-defense.
All the laws mentioned by Teret were controlled for in both
pieces.
Claim #4: "Knowing the exact
date that each `shall issue' law took effect is critically important
to measuring its impact -- yet the study includes some errors in
these dates."
I relied on a paper published in the Tennessee Law Review (Spring
1995) by Clayton Cramer and David Kopel to determine when different
states adopted shall issue laws. A separate Nexis data base search
was also conducted to determine the exact date of adoption.
Because of different interpretations over whether
a particular law constituted a shall issue law, the results were
tested to see whether defining Maine and Virginia as shall issue
states made a difference and it did not (in the original paper see p.
12, fn. 34 and p. 19, fn. 49 and in my book see p. 201, fn. 5).
In any case, I agree with Cramer and Kopel's
classification of state laws. Virginia's 1988 law explicitly uses the
term "shall-issue," and, with the exception of three counties, the
state followed that rule.
Claim #5: "The study does
not consistently define what it is evaluating."
Again we followed Cramer and Kopel in defining
state laws. However, how Connecticut and Alabama adopted their laws
decades before the sample period [1977 to 1994] and thus were
not involved in any of the before-and-after comparisons of shall
issue laws that I focused on.
For a more complete response to my critics, please see Chapter 7 in my newly released book More Guns, Less Crime: Understanding Crime and Gun Control Laws (University of Chicago Press, 1998).
D. Friedman's Home Page